How to setup Docker Monitoring
Learn how to set up Docker monitoring using tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and cAdvisor. Discover essential metrics to track, steps to configure monitoring tools, and how to set up alerts for maintaining a healthy Docker environment.

Docker monitoring servers and containers is becoming necessary as we provision more Docker hosts and containers. This tutorial will teach you how to combine several components to achieve Docker monitoring.
Components for Docker Monitoring
Before we begin, let's define the Docker installation assumptions. Docker should be installed, configured, and running on your target host. Please ensure you can connect to your Docker host with a Web Browser locally or over a Public IP. The rest of the Tutorial we will refer to this as the DockerIP. The below components will be used to create our Docker Monitoring solution.
cAdvisor - Google has been using containers for quite some time and created cAdvisor to help monitor its infrastructure. This single tool alone is an amazing monitoring tool. It monitors not only your Docker containers but also the Docker host without any configuration by just running the cAdvisor container on your Docker host. Be sure to check out the cAdvisor GitHub for more documentation on the API and different configuration options.
InfluxDB - InfluxDB is a distributed time series database. cAdvisor only displays realtime information and doesn't store the metrics. We need to store the monitoring information that cAdvisor provides in order to display a time range other than realtime.
Grafana Metrics Dashboard - The Grafana Dashboard allows us to pull all the pieces together visually. This powerful Dashboard allows us to run queries against the InfluxDB and chart them accordingly in a very nice layout.
Installation of Docker Monitoring
Now that we have an overview of the different components involved in our Docker Monitoring setup, let's start pulling it all together.
We will start with the InfluxDB first and work towards connecting the cAdvisor.
- Install the InfluxDb. We use the default settings below and name the container influxsrv which we will use later on for linking.
sudo docker run -d -p 8083:8083 -p 8086:8086 --expose 8090 --expose 8099 --name influxsrv tutum/influxdb
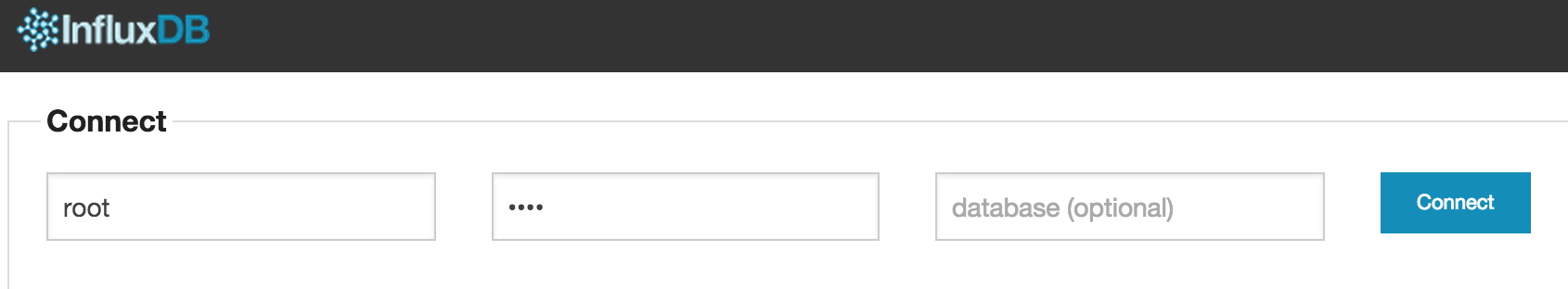
Let's test quickly that our InfluxDB installed correctly. Navigate to your http://DockerIP:8083
Use the credentials below to login to InfluxDB:
Username - root
Password - root
- Install the cAdvisor container and link it to the InfluxDB container.
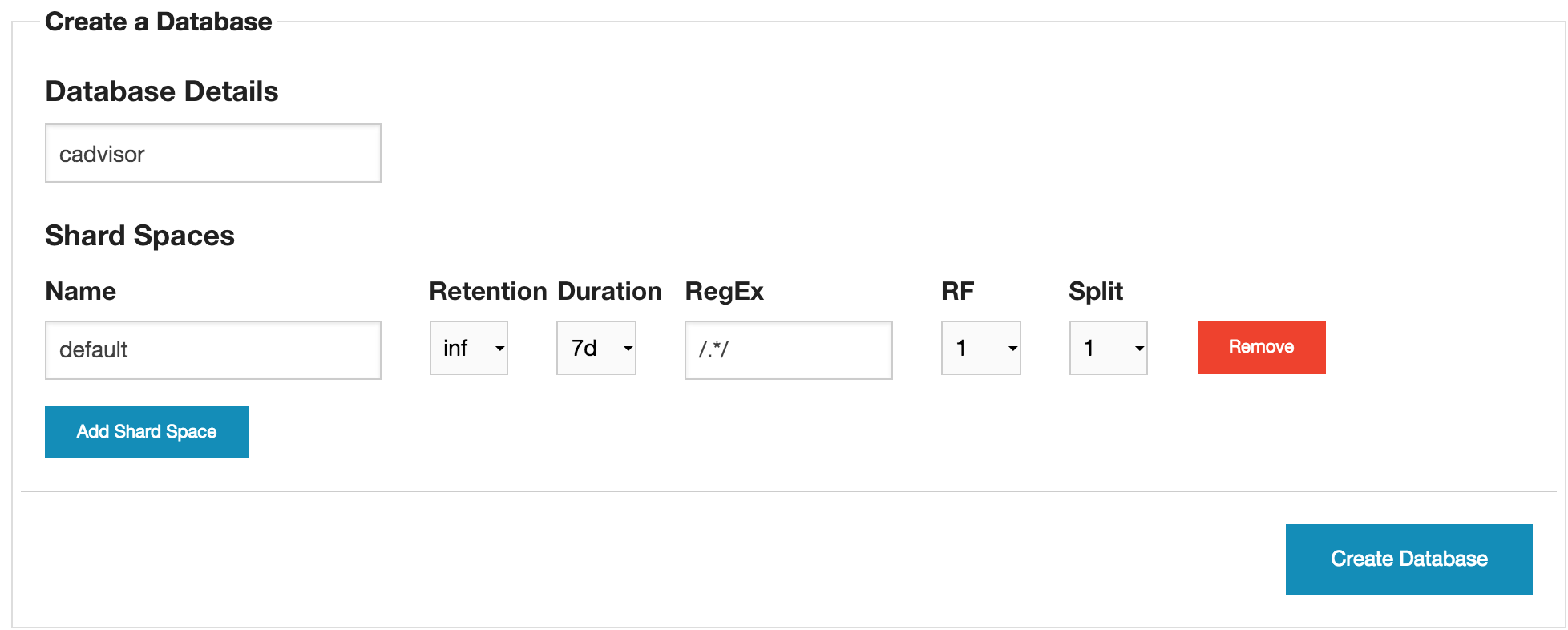
Create the cadvisor Database
After logging into InfluxDB click on the Databases link at the top of the screen. Type the name cadvisor for the Database name and click Create Database.
sudo docker run --volume=/:/rootfs:ro --volume=/var/run:/var/run:rw --volume=/sys:/sys:ro --volume=/var/lib/docker/:/var/lib/docker:ro --publish=8080:8080 --detach=true --link influxsrv:influxsrv --name=cadvisor google/cadvisor:latest -storage_driver_db=influxdb -storage_driver_host=influxsrv:8086
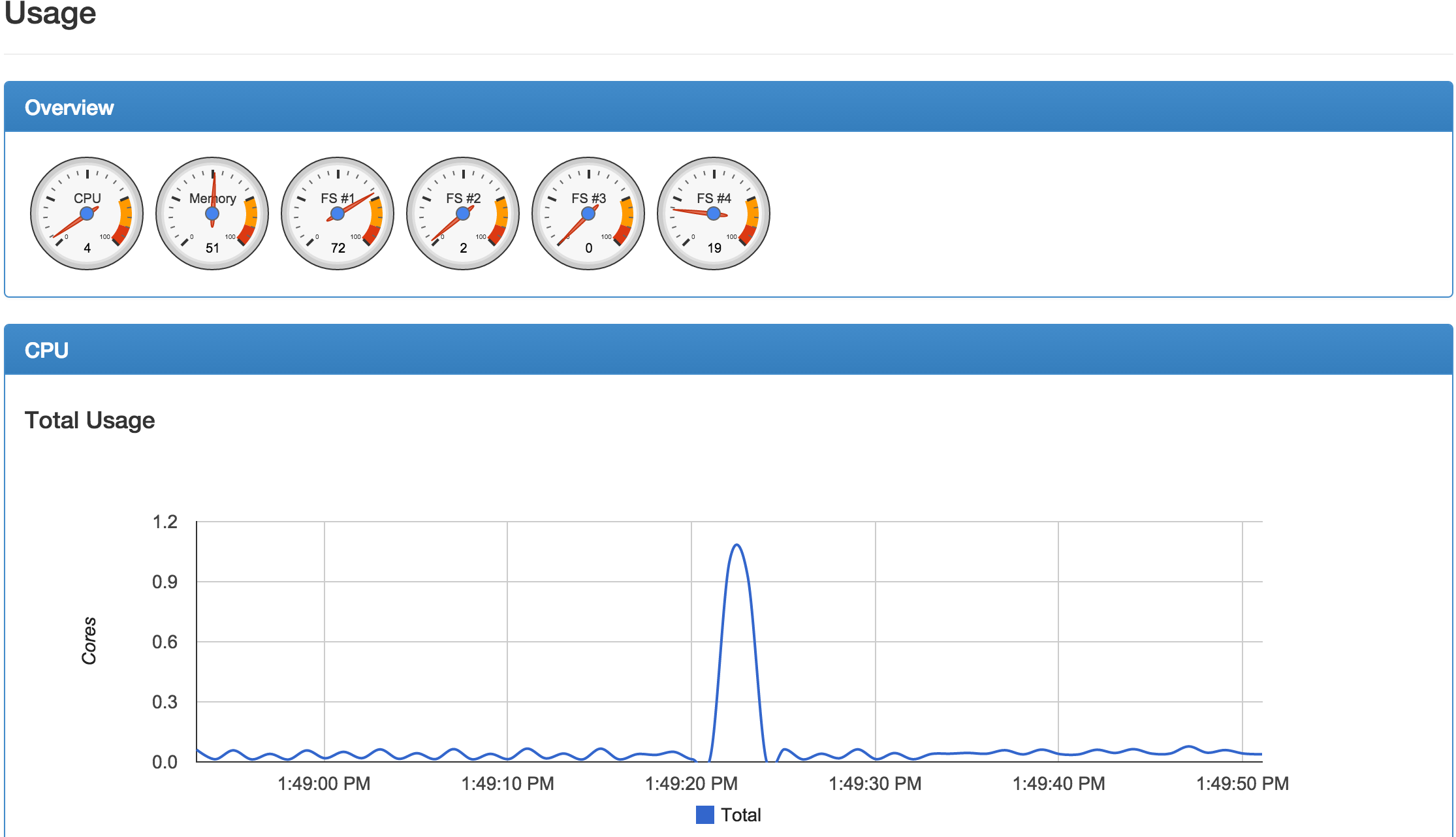
Once the cAdvisor container has been installed and running you can now navigate to the http://DockerIP:8080 For example, http://192.168.10.1:8080 You should now see the cAdvisor gathering statistics on your Docker host and containers.
- Install the Grafana Dashboard and link it to the InfluxDB container:
sudo docker run -d -p 3000:3000 -e INFLUXDB_HOST=localhost -e INFLUXDB_PORT=8086 -e INFLUXDB_NAME=cadvisor -e INFLUXDB_USER=root -e INFLUXDB_PASS=root --link influxsrv:influxsrv --name grafana grafana/grafana - Login to Grafana and configure the Data Sources.
Navigate to http://DockerIP:3000
Username - admin
Password - admin - Connect the InfluxDB to the Grafana Dashboard:
Once logged in click on the Grafana icon(Fireball) in the upper left hand corner of the GUI. This should pop out a sidebar menu. Click on Data Sources.
Next, click on Add New Data Source at the top of the screen.
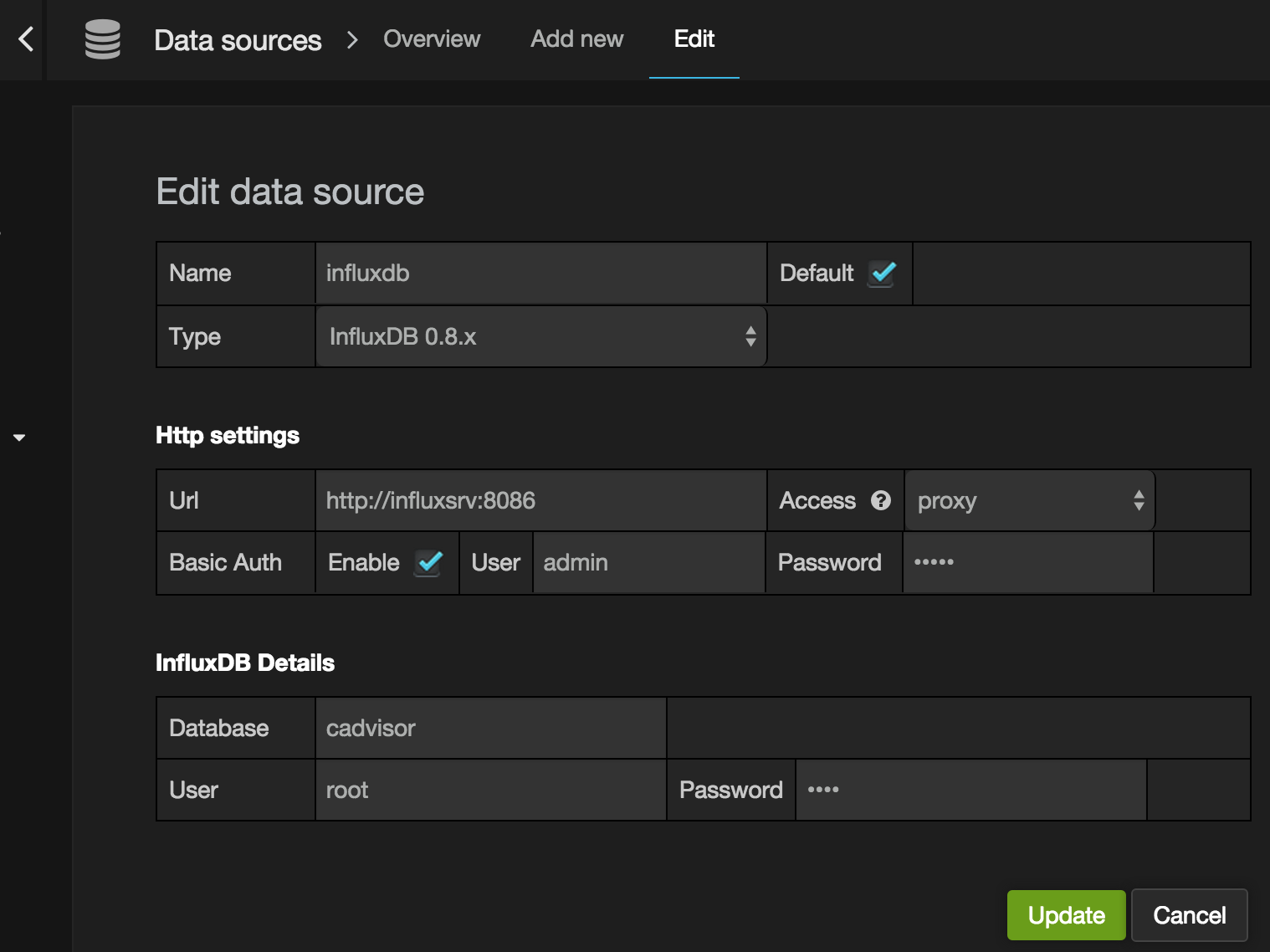
Fill in the following information in the Data Source screen:
Data Source Settings
Name: influxdb
Type: InfluxDB 0.8.x
Be sure to check default box.
Http settings
Url: http://influxsrv:8086 (This is the name we specified when createing the link on the Grafana container)
Access: proxy
Basic Auth: Enabled
User: admin
Password: admin
InfluxDB Details
Database: cadvisor (Or the name you specified when creating the database in step 2)
User: root
Password: root
You should now have an established connection to the InfluxDB which we will test in the next section.
Configuring Grafana for Docker Monitoring
Now comes the fun part. Let's setup our first Dashboard with Grafana and visualize the data coming from the cAdvisor.
- Click on the Grafana icon once again (The Fireball icon upper left corner)
- Open the Dashboard menu --> Expand the Home Menu drop Down --> Click +New
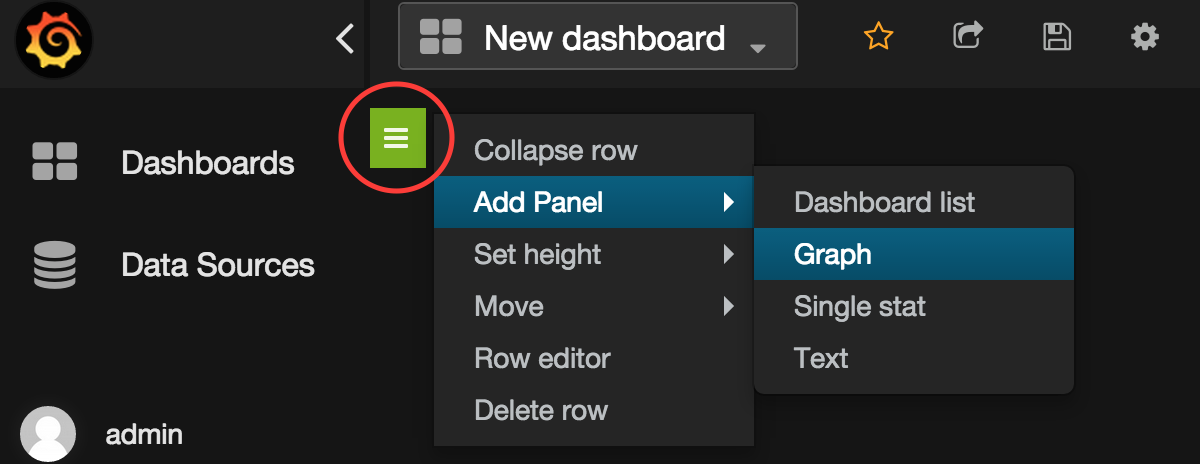
- We've now created a new Dashboard inside of Grafana. Let's create our first graph inside this Dashboard. Click the green vertical line as seen below in the screenshot circled in Red. This expands the row options for the Dashboard.
- Click Add Panel --> Graph
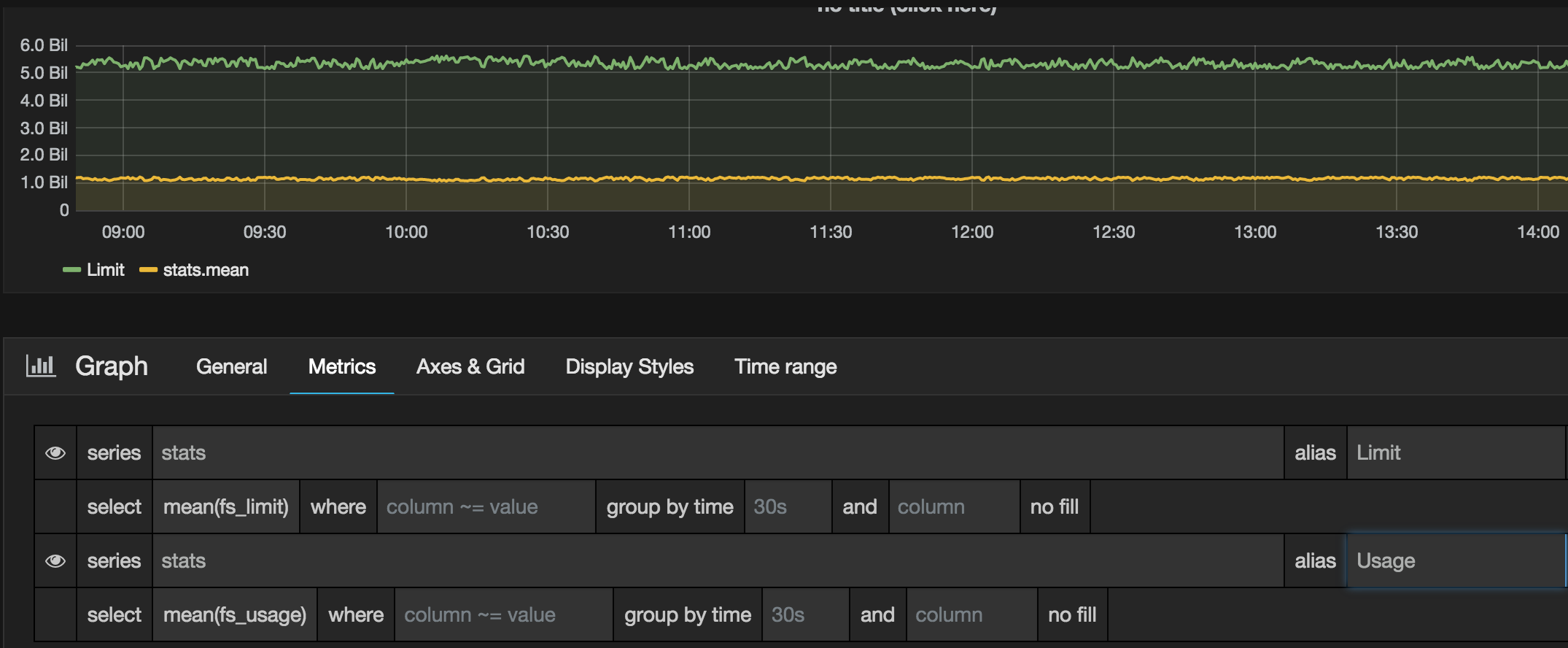
- It's time to write our first query for our graph. We will create a graph displaying the Filesystem storage limit and usage.
Query 1 - Fill in the following information inside the Graph screen:
series: stats
Click on "value" which will present you a drop down list of available series available inside of the InfluxDB.
select: mean(fs_limit)
Alias: Limit
Click the Title area of the new Graph you created where it says "no title (click here)" and click Edit
Query 2 - At the Bottom of Graph screen is an +Add Query button which allows us to add another metric to our graph.
series: stats
select: mean(fs_usage)
Alias: Usage
- Click on the General Menu and Change the Title of your Graph
- Click on the Axis & Grid Menu
Left Y Unit: Bytes
Your Chart should now display with the correct units. - Once finished like any other project be sure to save your work. Hit the Save icon a the top of the screen.
The queries seen in the sample screenshot can be found here - Docker Monitoring Queries
Docker Monitoring Conclusion
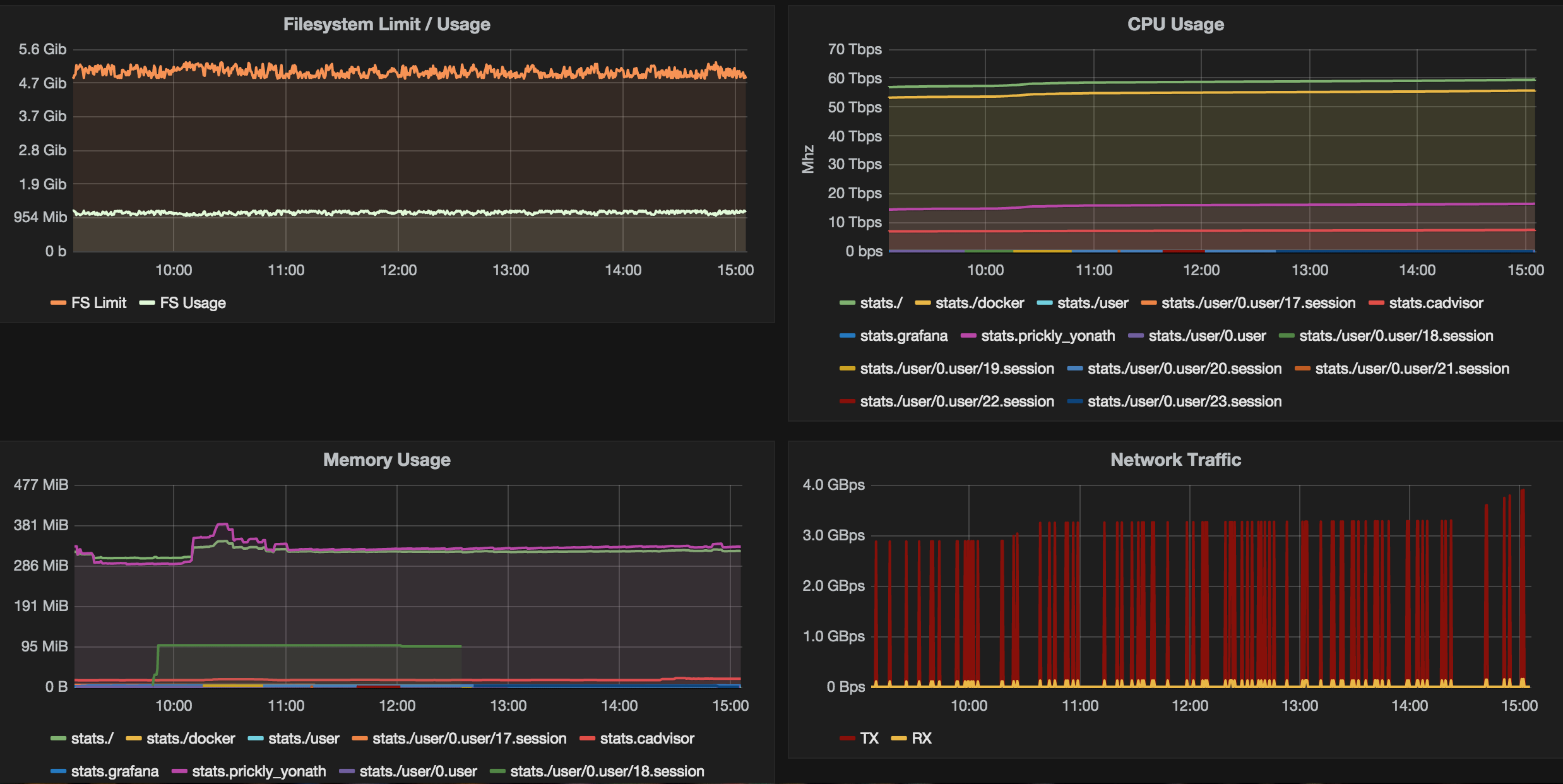
We have now built a single Grafana Dashboard with a Graph containing our Filesystem statistics. As you can see, it's straightforward to create multiple graphs to monitor our Docker Host and Containers.
Be sure to check out the Grafana Docs to learn more about the queries and functionality of Grafana. Take a look below at the screenshot, which shows the possibilities for creating some really interesting graphs (Bandwidth, CPU Usage per Container, Memory Usage, and Filesystem Limit/Usage).
Leave a comment below if you have any issues or questions.
Good Luck!
Troubleshooting
If you have trouble, this is for you. It took me quite some time to figure out all the settings and where the problems were with the connection from Grafana to InfluxDB. If you have issues with your Graphs, I highly recommend a Development Console in your Browser of choice.
With the development console, it's easy to see problems with your queries or connections to the InfluxDB container. For Example: Chrome Development Tools -> More Tools -> Javascript Console
Another workaround is using the IP address of the containers to resolve connection issues. However, if you restart the container the IP address changes so this is only a temp fix.
docker inspect <container name>
Search the output for the IP address which is under the Network Settings section as seen below:"NetworkSettings": { "Bridge": "docker0", "Gateway": "172.17.42.1", "GlobalIPv6Address": "", "GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0, "IPAddress": "172.17.0.54",
You can then replace the name that we used in Data Source settings we used above as a workaround. This worked for me until I fixed the links between containers.
FAQ Section: How to Set Up Docker Monitoring
Why is Docker monitoring important? Docker monitoring is crucial for ensuring the health and performance of your containerized applications. It helps detect and resolve issues, optimize resource usage, ensure uptime, and maintain the reliability and efficiency of your Docker environment.
What tools are best for monitoring Docker containers? Several tools are popular for monitoring Docker containers, including:
- Prometheus: Open-source monitoring and alerting toolkit.
- Grafana: Visualization tool often used with Prometheus for monitoring dashboards.
- cAdvisor: Provides insights into container resource usage and performance.
- Datadog: Cloud-based monitoring with comprehensive Docker integration.
- ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana): A powerful suite for logging and monitoring.
How do I set up Prometheus and Grafana for Docker monitoring? To set up Prometheus and Grafana for Docker monitoring:
- Install Prometheus: Use the official Docker image and configure the
prometheus.ymlfile to scrape metrics from your Docker environment. - Install Grafana: Use the official Docker image and configure it to use Prometheus as a data source.
- Configure Dashboards: Create and configure Grafana dashboards to visualize metrics collected by Prometheus, such as container CPU, memory usage, and network statistics.
What metrics should I monitor in my Docker environment? Key metrics to monitor in your Docker environment include:
- CPU Usage: Overall and per-container CPU utilization.
- Memory Usage: Total memory usage and per-container memory consumption.
- Network Traffic: Incoming and outgoing network traffic per container.
- Disk I/O: Read and write operations on disk storage.
- Container Health: Status of container health checks and restarts.
How can I set up alerts for Docker monitoring? To set up alerts for Docker monitoring:
- Use Prometheus Alertmanager: Configure Prometheus to send alerts to Alertmanager based on predefined rules.
- Define Alert Rules: Create alert rules in the
prometheus.ymlfile for metrics that exceed thresholds (e.g., high CPU usage). - Configure Alertmanager: Set up Alertmanager to send notifications via email, Slack, or other communication channels.
- Integrate with Grafana: Set up alerting in Grafana for visual and email alerts based on dashboard metrics.
Follow me
If you liked this article, Follow Me on Twitter to stay updated!



